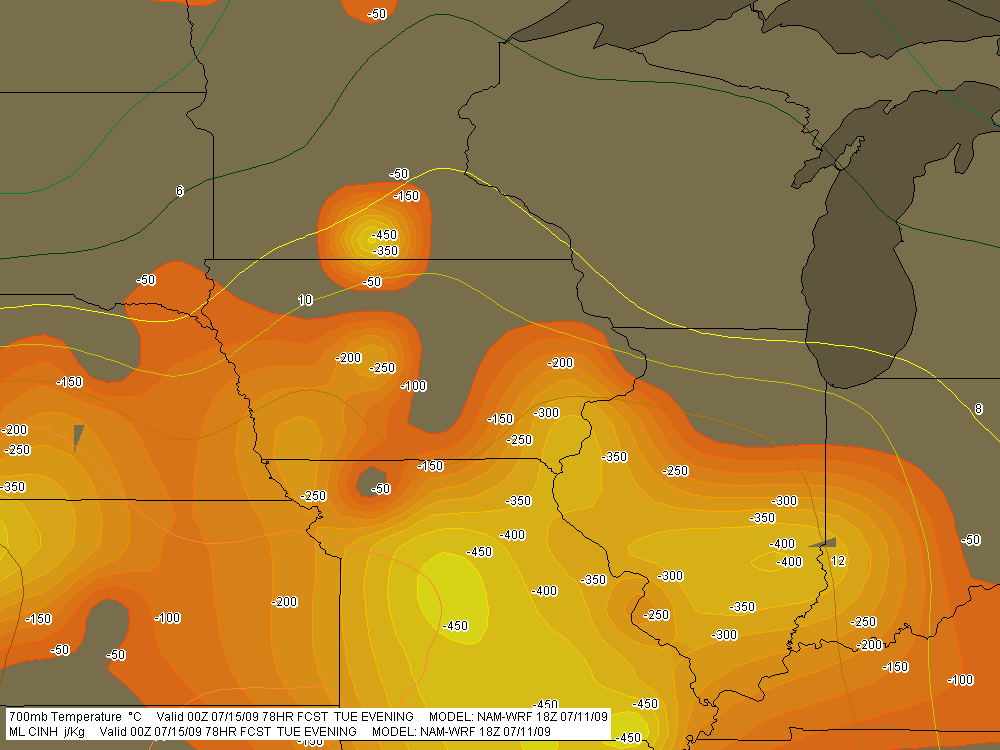
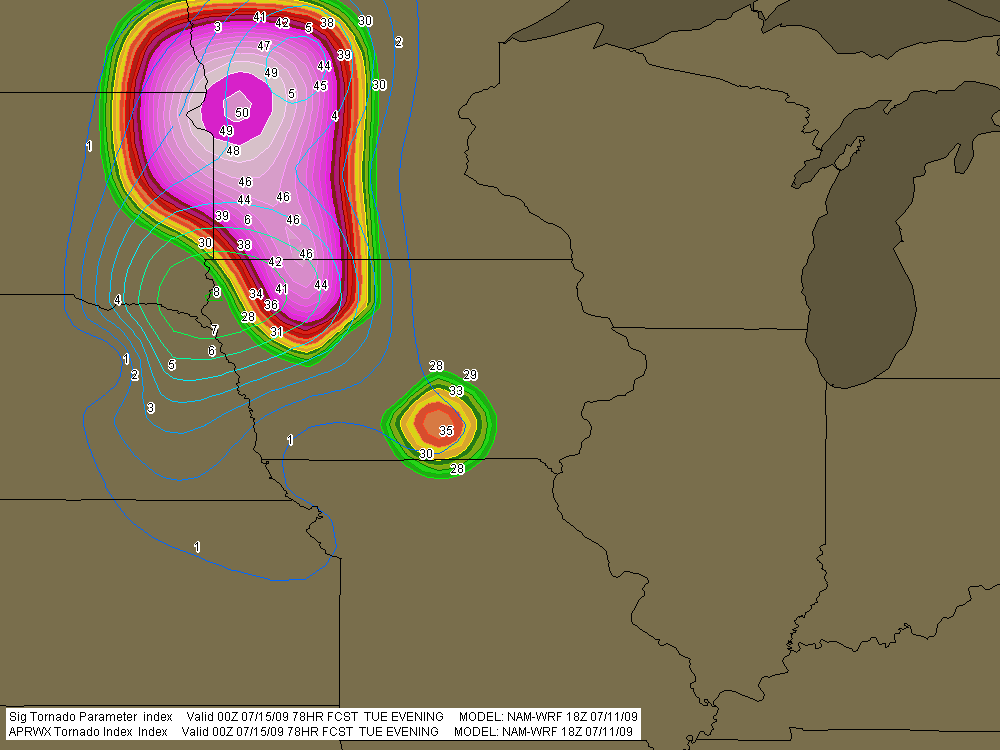
At last, the setup I’ve been waiting for–one that warrants dipping into my tight finances in order to make the 1,000-mile drive to the Southern Plains. To date, this present system has been a miserable disconnect between upper-level support and instability, with a nasty cap clamping down on the whole shebang. Last night it managed to cough up a solitary tornado in South Dakota. That was it. I’m not sure what today holds, but I haven’t seen anything to excite me about it or tomorrow.
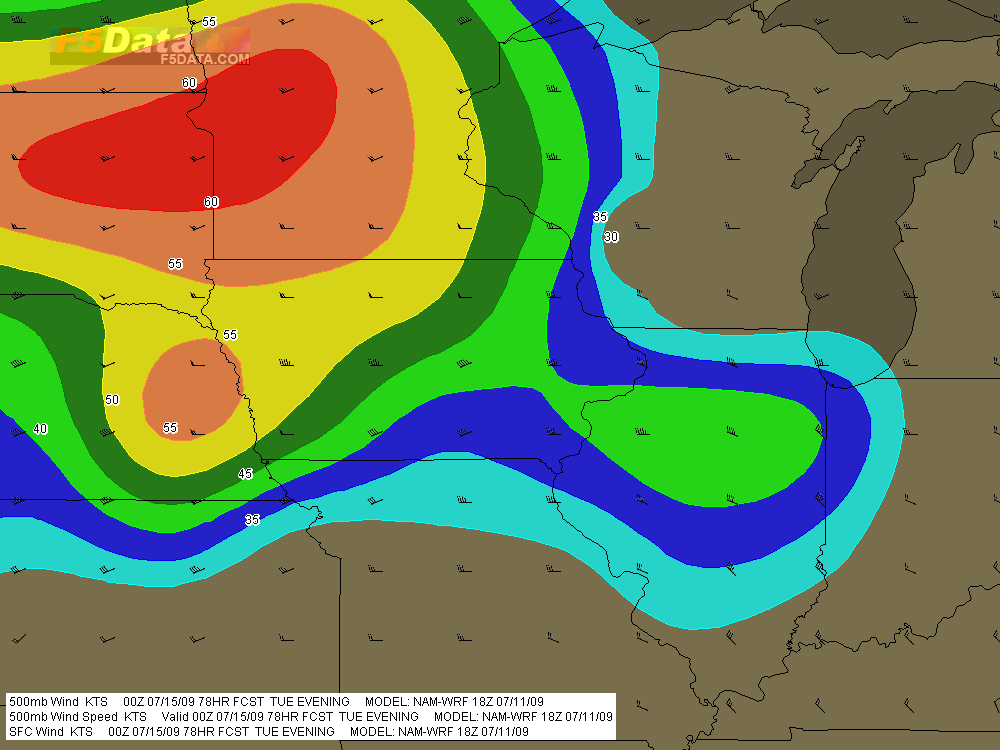
But Wednesday…ah, now we’re talking! The SPC places a large section of the Great Plains under a slight risk, and their discussions have been fairly bullish about the potential for a wide-scale event. At first I couldn’t see why. My mistake–I was looking at the NAM, which with straight southerly H5 winds has not provided the best PR for Wednesday’s setup. But once I glommed the GFS, I got a whole ‘nother picture, one which the SREF and Euro corroborated.
That was last night. I haven’t looked at today’s SREF, and the new ECMWF gives me a slight pause as its now somewhat negative tilt has slightly backed the mid-levels from the previous run. But only slightly. The H5 winds still have a nice southwesterly flow, and taking the three models together, everything you could ask for is lining up beautifully for tornadoes in the plains.
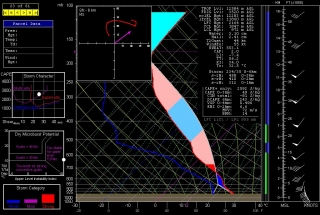
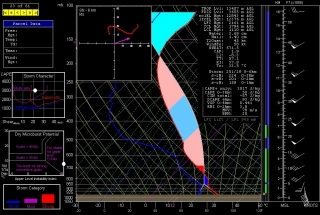
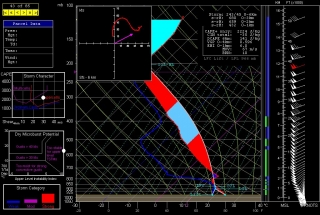
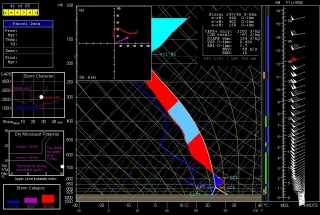
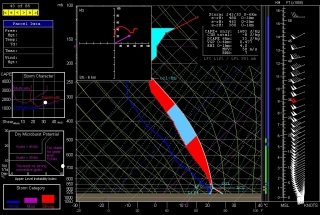
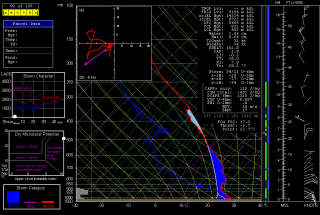
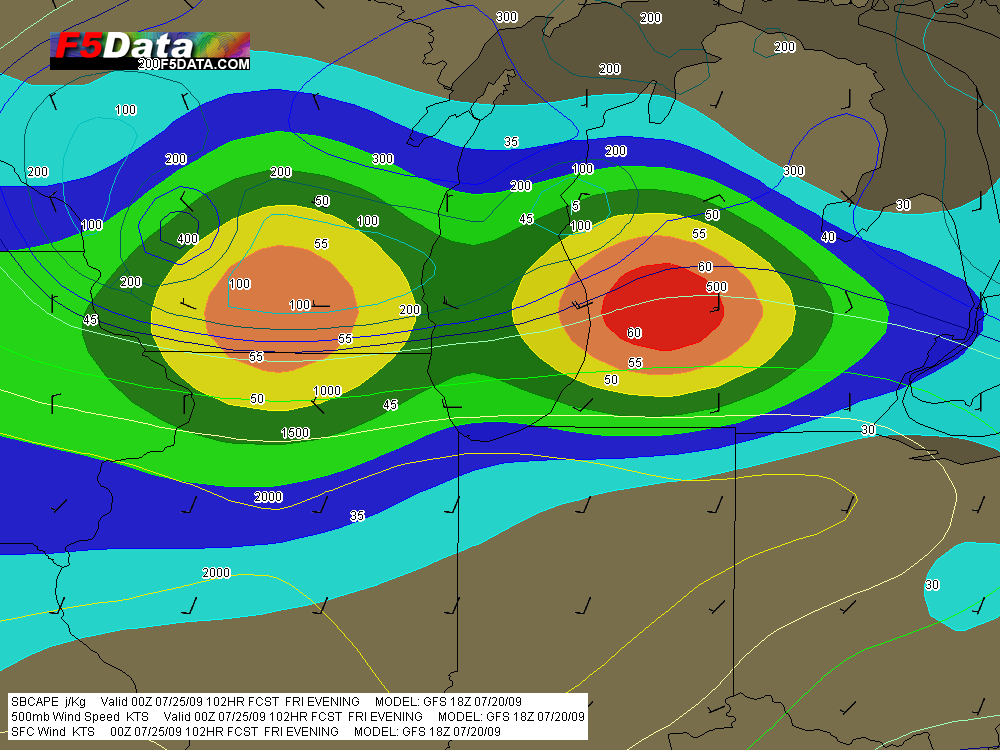
The event promises to be widespread, with a robust dryline stretching from a triple point in southwest Kansas south through Oklahoma and Texas. Positioned near a dryline bulge, Enid, Oklahoma has drawn my attention for the last couple of GFS runs. Check out this model sounding for 00Z and tell me what’s not to like about it. Everything is there, including a voluptuous hodograph and 1 km SRH in excess of 300 m^2/s^2.
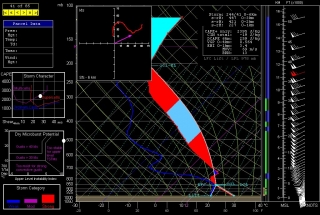
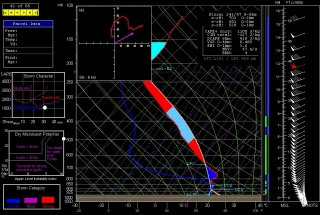
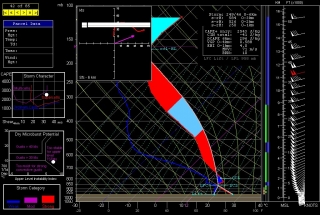
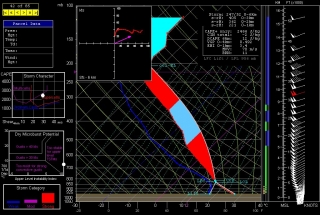
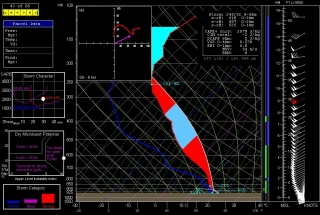
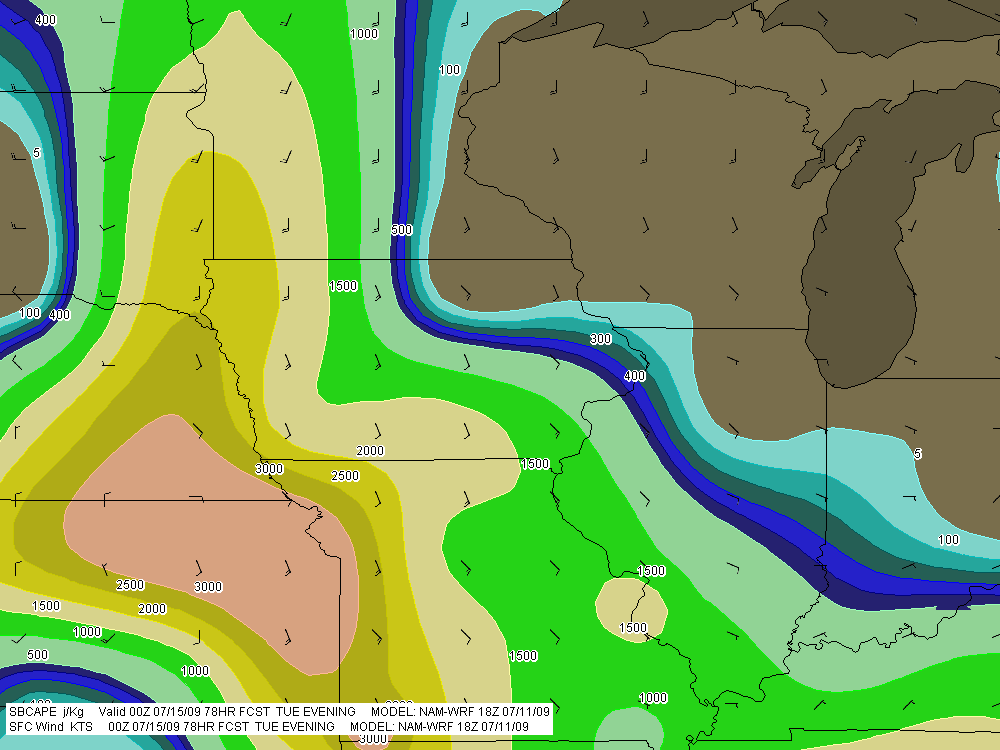
Other places in the region also look good, though. Farther south in Texas, Wichita Falls shows potential. Helicity isn’t as persuasive as Enid, but the CAPE tops 3,000 J/kg and there’s less
convective inhibition. Here’s the sounding for you to compare with Enid.I haven’t been as drawn to Kansas so far, but with the triple point perched there, storms are bound to fire up just fine in the Sunflower State. The details will work themselves out between now and Wednesday evening. Significantly, the tyrannical cap of the previous few days no longer appears to be an issue.
The bottom line is–it’s time to head West! This evening I’m taking off for the plains with my long-time chase buddy Bill. At last! Time to sample what the dryline has to offer, and–now that I’m equipped with a great HD camcorder–finally get some quality footage of a tornado or two.
There’s no place like the Great Plains! YeeeeHAW!!!!!